top of page
MAGNETORHEOLOGICAL FLUIDS
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |
Location - National Institute of Technology Karnataka
Mentor - Dr.Hemantha Kumar (Assistant Professor - Mechanical Department)
Project Abstract -
The main aim of this project is to investigate the performance of Magnetorheological
dampers used as semi-active suspension devices in quarter car and half car models to improve ride comfort, road holding and suspension working of a vehicle traversing on a rough
road at constant velocity.
The report includes basics of suspension systems in a vehicle and how suspension systems work. After that different types of suspension systems are introduced, followed by reasons to why semi-active suspension systems are preferred to passive and active suspension systems. It also includes a short introduction on Magneto-Rheological fluids and their construction and working.
Our project involves using Bouc-Wen and Modified Bouc-Wen models to characterize the hysteric behavior of MR fluid dampers. The Bouc-Wen model parameters are optimally calculated from the experimental hysteric behavior obtained by dynamic tests performed on the fabricated damper for different input currents by minimizing the mean square error between analytical and experimental results. This is done by solving the multi-objective optimization problem through the combination of Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA II) and Pareto optimal scheme.
The Bouc-Wen and Modified Bouc-Wen models are modeled in MATLAB Simulink and used in the optimization technique to find the optimal parameter values by comparing it with the given experimental values. This model is used to calculate the damper force from input displacement and velocity as a sinusoidal function. Once the optimal parameters are obtained the Simulink model is used to calculate the damper force on the MR damper for any input current.
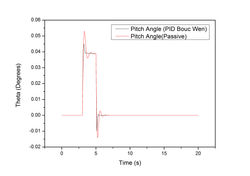
A quarter car and half car model are generated in MATLAB Simulink. These models are used to plot the response curves when subjected to various road profile inputs such as step, pulse and monte-carlo simulation. These models are then compared with a semiactive suspension system involving an MR damper which is controlled with the help of a suitable controller and modeled using Bouc-Wen and Modified Bouc-Wen models to show the difference between a passive system and a semi-active suspension system.
Further the quarter car system is modeled using ADAMS and co-simulated with MATLAB.The response curves are compared with the MATLAB mathematical model to find the accuracy of the co-simulation and compared with passive suspension models also developed using ADAMS.
bottom of page